Business networks today are often inefficient because each participant in the network keeps records, or a ledger, of all transactions between all the parties that the business interacts with. This process is expensive because of duplication of effort and intermediaries adding costs for their services. One solution to this problem is blockchain, which provides a distributed ledger technology that are shared in a way that allows any participant on the network to see the one system of record, or ledger. By using blockchain technology, businesses can benefit from a more efficient transfer of goods and services. Blockchain increases the speed of transactions, slash auditing costs, reduces risk of cyberattacks, and increases trust.
- Working principle of blockchain
- Characteristics of Blockchain
- Applications/Use-cases
- Bitcoin
- Useful Resources
Working principle of blockchain
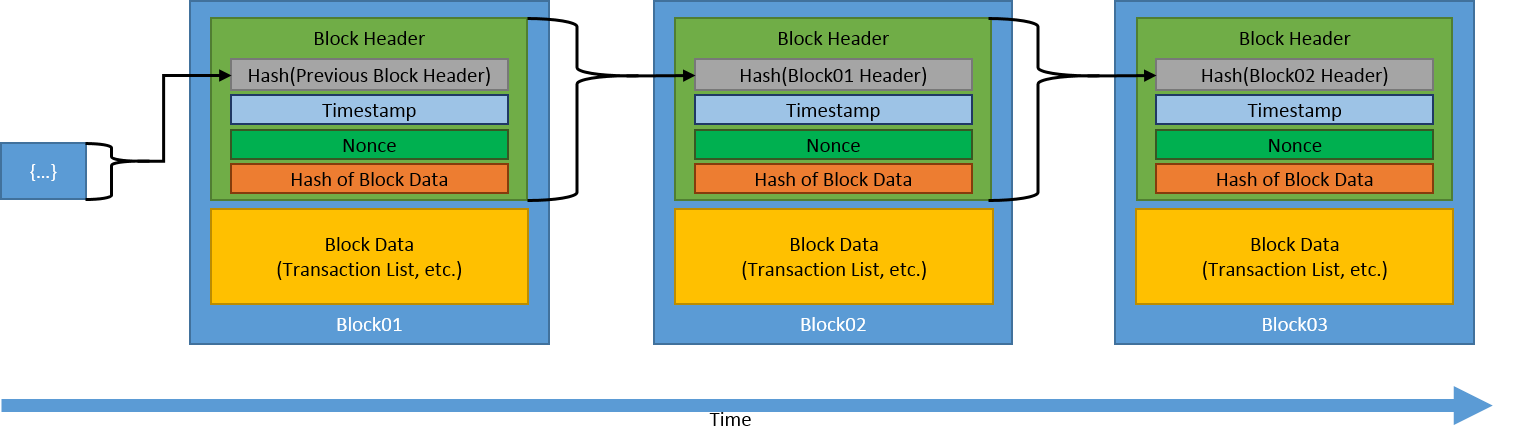
A blockchain contains blocks (also called records) that are tied or chained in a sequence in a secured way so as to strongly resist to altertion or changes.
 |
|---|
| Blockchain (Credit: NIST) |
Each current block contains three key things – data, hash of the current block and hash of the previous block.
-
The data stored inside the block depends on the type of blockchain. For example, data in a bitcoin block stores the details about the transaction such as sender, reciever and the amount of coins.
-
The hash of the current block is the identifier of the block and all of its contents. It can be seen as similar to a fingerprint and is unique for each block. Once the block is created, its hash is being calculated. Each time something is altered in the block, another hash is being created for that block.
-
The hash of the previous block consists of the identification of the previous block thus effectively forming the chain within blocks and this serves the purpose of providing the security to the blockchain technique. Changing the current block will make the subsequent blocks invalid as the current block will change the hash and the next block will have an invalid pointer to the current block.
Even though the hash function provides a good security, it is still vulnerable to spammers trying to modifying the current block and recalculating the hashes for the blocks following it. In order to circumvent this issue, there is a mechanism called proof-of-work that is used to secure our blockchain against spammers and people trying to tamper with the blocks.
Each of the transaction between two parties is validated and added block-by-block in a blockchain by miners. A miner solves a complex, mathematical problem in order to validate and adding of the block to the blockchain. The process of solving the complex, mathematical problem is called proof-of-work and the process of adding the block to the sequence is called mining.
Blockchain for business has several advantages:
- Saves time
- Removes cost
- Reduces risk
- Increases trust
Characteristics of Blockchain
Consensus: It implies that all relevant parties agree that the information contained in the ledger about the business network is true
Provenance: It implies that the ledger contains all the relevant information, starting from the beginning of relationship within the business network.
Immutability: It implies that once the transaction has occurred within the business network and the record book (ledger) has registered it, it cannot be changed.
Finality: It implies about the guarantee that the transaction history within the business network will never be changed.
Applications/Use-cases
Some of the use-cases of blockchain are:
-
For financial services network, a business network that runs on a blockchain can speed up transaction processes and audits. That in turn reduces costs and can lead to greater customer satisfaction. A business that runs a supply-chain network can benefit from blockchain by reducing errors in shipments, have better tracking or materials, and reduce the risk of illicit tampering of records.
-
In heatlhcare industry, blockchain can be used to store sensitive and private information of patients in such a secure manner so that they can be accessed by only the concerned and authorized entities like doctors, healthcare provider and patients.
-
Blockchain can be used in securing intellectual property like creative thoughts and ideas that people transmit into the paper and are worried about getting it stolen or claiming of rights. For each doument, the blockchain can create a unique secured, hash function that proofs the validity and existentiality of the document along with the timestamp. This process of certification of document is often described as proof of existence.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is an unregulated, censorship-resistant, popular shadow currency. Often times, it is heard that Bitcoin = Blockchain, however, this is not true. It is basically the first blockchain application or the pioneer of blockchain technology.
A bitcoin can be understand as an entry on a global, public ledger called blockchain. The blockchain records every bitcoin transaction that has ever happened. The bitcoin blockchain that records bitcoin transactions. It is implemented as a chain of blocks, each block containing a hash of the previous block up to the genesis block of the chain.
Bitcoin value follows the law of supply and demand. It works on the following guideline – the higher the demand, the higher the price; the lower the demand, the lower the price. Since the demand of bitcoin can increase and decrease in an uncertain fashion, bitcoin price is highly volatile. We can also track this volatile characteristic and overall trend from the below bitcoin price watcher that monitors the current price.
Bitcoin uses the SHA256 (Secure hash algorithm 256 bit) algorithm for producing hashes for transactions which is why it is termed as cryptocurrency. Computers that were specifically designed to solve the SHA256 hash problems, take on average, about 10 minutes to guess the solution to each one.
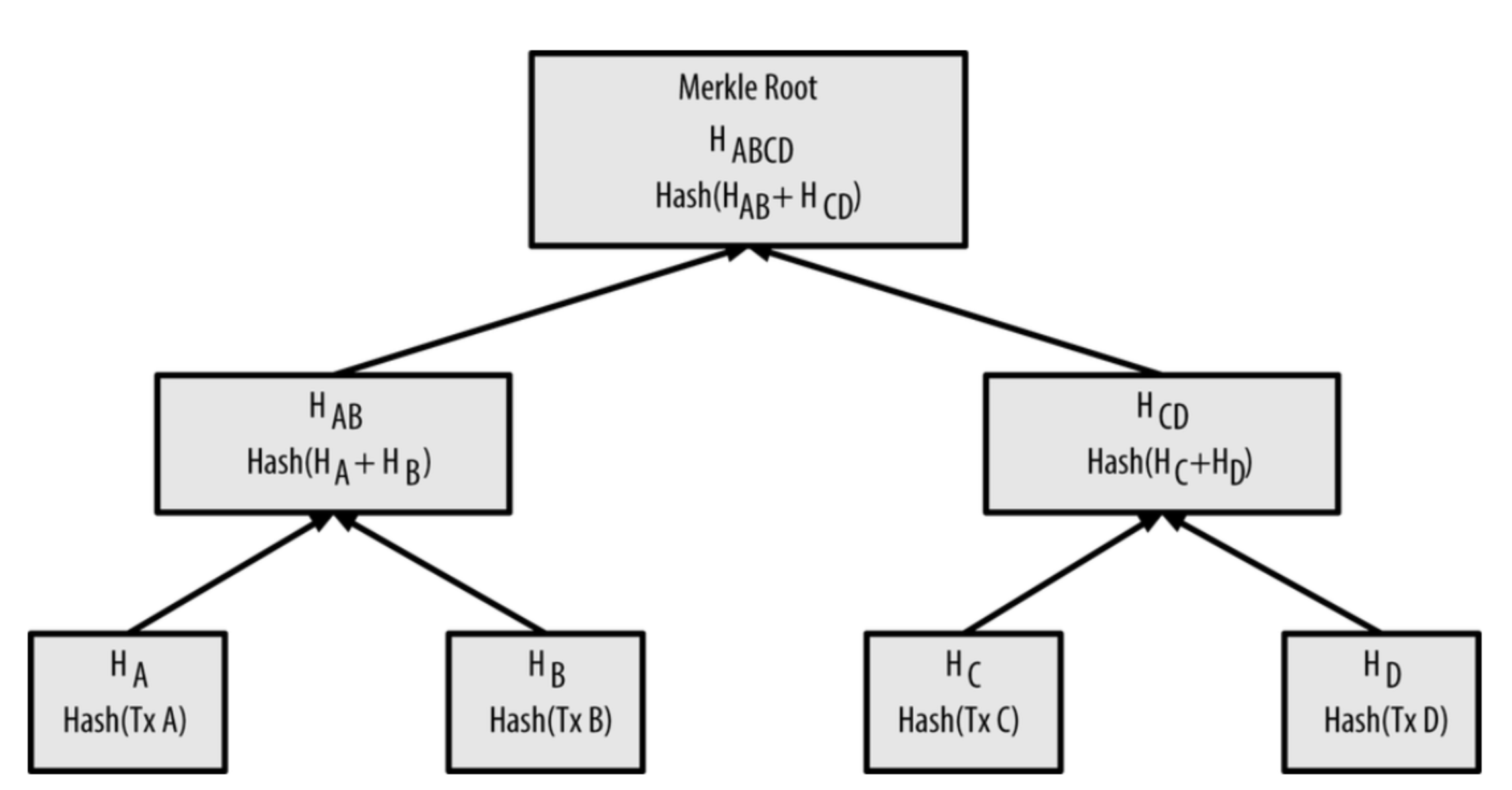
To ensure the data integrity in the blockchain, merkle trees are used. Each block in a blockchain can contain multiple transactions, each of which contains data.
 |
|---|
| Merkel Tree (Credit: Mastering Bitcoin course by Andreas Antonopoulos) |
In the above merkel tree, there are four transactions Tx A, Tx B, Tx C and Tx D. Each of the data in these four transactions are passed through a hash function to generate four unique hashes \(H_A\), \(H_B\), \(H_C\) and \(H_D\) one for each transaction.
Pairs of hashes are combined and pass through the hash function again to generate two hashes of hashes (\(H_{AB}\), \(H_{CD}\)). These two hashes are combined again and pass through the hash function which results in a single root hash (\(H_{ABCD}\)) producing a complete merkel tree. This tree can detect even the slightest changes in the transactions of a block by re-running the process for each transaction and comparing the results to the original root hash.
Useful Resources
Making Blockchain real for business